
Please, refer to file doc/glpk.pdf of the GLPK source distribution for a detailed description of the methods and constants.
To be able to use the JNI library in a Java program it has to be loaded. The path to dynamic link libaries can specified on the command line when calling the Java runtime, e.g.
java -Djava.library.path=/usr/local/lib/jni/libglpk_java
The following code is used in class GLPKJNI to load the JNI library (for version 4.65 of GLPK):
static {
try {
if (System.getProperty("os.name").toLowerCase().contains("windows")) {
// try to load Windows library
#ifdef GLPKPRELOAD
try {
System.loadLibrary("glpk_4_65");
} catch (UnsatisfiedLinkError e) {
// The dependent library might be in the OS library search path.
}
#endif
System.loadLibrary("glpk_4_65_java");
} else {
// try to load Linux library
#ifdef GLPKPRELOAD
try {
System.loadLibrary("glpk");
} catch (UnsatisfiedLinkError e) {
// The dependent library might be in the OS library search path.
}
#endif
System.loadLibrary("glpk_java");
}
} catch (UnsatisfiedLinkError e) {
System.err.println(
"The dynamic link library for GLPK for Java could not be"
+ "loaded.\nConsider using\njava -Djava.library.path=");
throw e;
}
}GLPKPRELOAD is enabled in the Windows build files by default. For POSIX systems it can be enabled by
./configure --enable-libpath
If the JNI library can not be loaded, you will receive an exception java.lang.UnsatisfiedLinkError.
When illegal parameters are passed to a function of the GLPK native library an exception GlpkException is thrown. Due to the architecture of GLPK all GLPK objects are invalid when such an exception has occured.
GLPK for Java registers a function glp_java_error_hook() to glp_error_hook() before calling an GLPK API function. If an error occurs function glp_free_env() is called and a long jump is used to return to the calling environment. Then function glp_java_throw() is called which throws a GlpkException.
For network problems additional data like capacity and cost of arcs or the inflow of vertics has to be specified. The GLPK library does not provide data structures. In GLPK for Java classes glp_java_arc_data and glp_java_vertex_data are provided.
When creating a graph the size of the structures for these classes has to be specified. In some routines the offsets to individual fields in the structures are needed. The following constants have been defined:
For accessing vertices method GLPK.glp_java_vertex_get can be used.
For accessing the data areas of arcs and vertices methods GLPK.glp_java_arc_get_data, GLPK.glp_java_vertex_data_get, and GLPK.glp_java_vertex_get_data can be used.
glp_arc arc;
glp_java_arc_data adata;
glp_java_vertex_data vdata;
glp_graph graph =
GLPK.glp_create_graph(
GLPKConstants.GLP_JAVA_V_SIZE,
GLPKConstants.GLP_JAVA_A_SIZE);
GLPK.glp_set_graph_name(graph,
MinimumCostFlow.class.getName());
int ret = GLPK.glp_add_vertices(graph, 9);
GLPK.glp_set_vertex_name(graph, 1, "v1");
GLPK.glp_set_vertex_name(graph, 2, "v2");
GLPK.glp_set_vertex_name(graph, 3, "v3");
GLPK.glp_set_vertex_name(graph, 4, "v4");
GLPK.glp_set_vertex_name(graph, 5, "v5");
GLPK.glp_set_vertex_name(graph, 6, "v6");
GLPK.glp_set_vertex_name(graph, 7, "v7");
GLPK.glp_set_vertex_name(graph, 8, "v8");
GLPK.glp_set_vertex_name(graph, 9, "v9");
vdata = GLPK.glp_java_vertex_data_get(graph, 1);
vdata.setRhs(20);
vdata = GLPK.glp_java_vertex_data_get(graph, 9);
vdata.setRhs(-20);
arc = GLPK.glp_add_arc(graph, 1, 2);
adata = GLPK.glp_java_arc_get_data(arc);
adata.setLow(0); adata.setCap(14); adata.setCost(0);
...
GLPK.glp_write_mincost(graph,
GLPKConstants.GLP_JAVA_V_RHS,
GLPKConstants.GLP_JAVA_A_LOW,
GLPKConstants.GLP_JAVA_A_CAP,
GLPKConstants.GLP_JAVA_A_COST,
"mincost.dimacs");
GLPK.glp_delete_graph(graph);
The MIP solver provides a callback functionality. This is used to call method callback of class GlpkCallback. A Java program can listen to the callbacks by instantiating a class implementing interface GlpkCallbackListener and registering the object with method addListener() of class GlpkCallback. The listener can be deregistered with method removeListener(). The listener can use method GLPK.glp_ios_reason() to find out why it is called. For details see the GLPK library documentation.
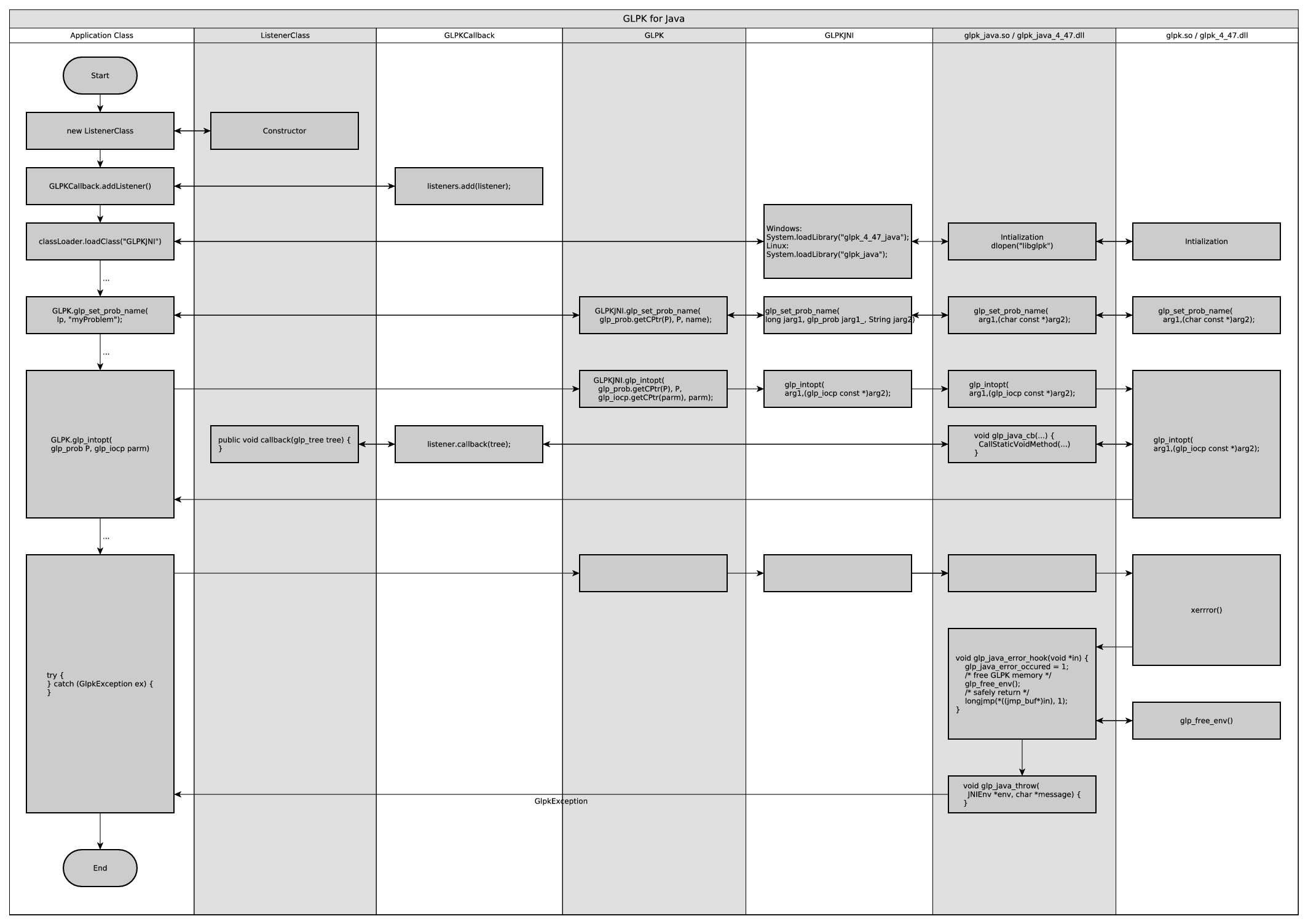
GLPK provides a hook for terminal output. A Java program can listen to the callbacks by instantiating a class implementing interface GlpkTerminalListener and registering the object with method addListener() of class GlpkTerminal. The listener can be dregistered with method removeListener(). After a call to glp_free_env() class GlpkTerminal has to registered again by calling GLPK.glp_term_hook(null, null). glp_free_env() is called if an exception GlpkException occurs.
Method GLPK.glp_java_error(String message) can be used to abort any call to the GLPK library. An exception GlpkException will occur. As GLPK is not threadsafe the call must be placed in the same thread as the initial call that is to be aborted. The output() method of a GlpkTerminalListener can be used for this purpose.
Method void GLPK.glp_java_set_msg_lvl(int msg_lvl) can be used to enable extra output signaling when a GLPK library function is entered or left using value with GLPKConstants.GLP_JAVA_MSG_LVL_ALL. The output is disabled by a call with value GLPKConstants.GLP_JAVA_MSG_LVL_OFF.
Method void GLPK.glp_java_set_numeric_locale(String locale) can be used to set the locale for numeric formatting. When importing model files the GLPK library expects to be using locale â€Câ€.
The GLPK library is not thread safe. Never two threads should be running that access the GLPK library at the same time. When a new thread accesses the library it should call GLPK.glp_free_env(). When using an GlpkTerminalListener it is necessary to register GlpkTerminal again by calling GLPK.glp_term_hook(null, null).
When writing a GUI application it is advisable to use separate threads for calls to GLPK and the GUI. Otherwise the GUI cannot react to events during the calls to the GLPK libary.